
Vulvar cancer is a form of cancer that manifests in the external part of the female genitalia, known as the vulva.
While it accounts for a small fraction of all cancer diagnoses in women, its impact on the lives of patients and their families can be profound.
Here, we’ll explore the ins and out of vulvar cancer, including the criteria that gynecologists use to diagnose vulvar cancer, vulvar cancer treatments, and ways to prevent vulvar cancer.
Vulvar cancer, a malignancy that arises on the outer lips of the female genitalia, specifically on the labia majora and the labia minora.
According to the American Cancer Society, while vulvar cancer accounts for only about 0.6% of all cancers in women, its early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
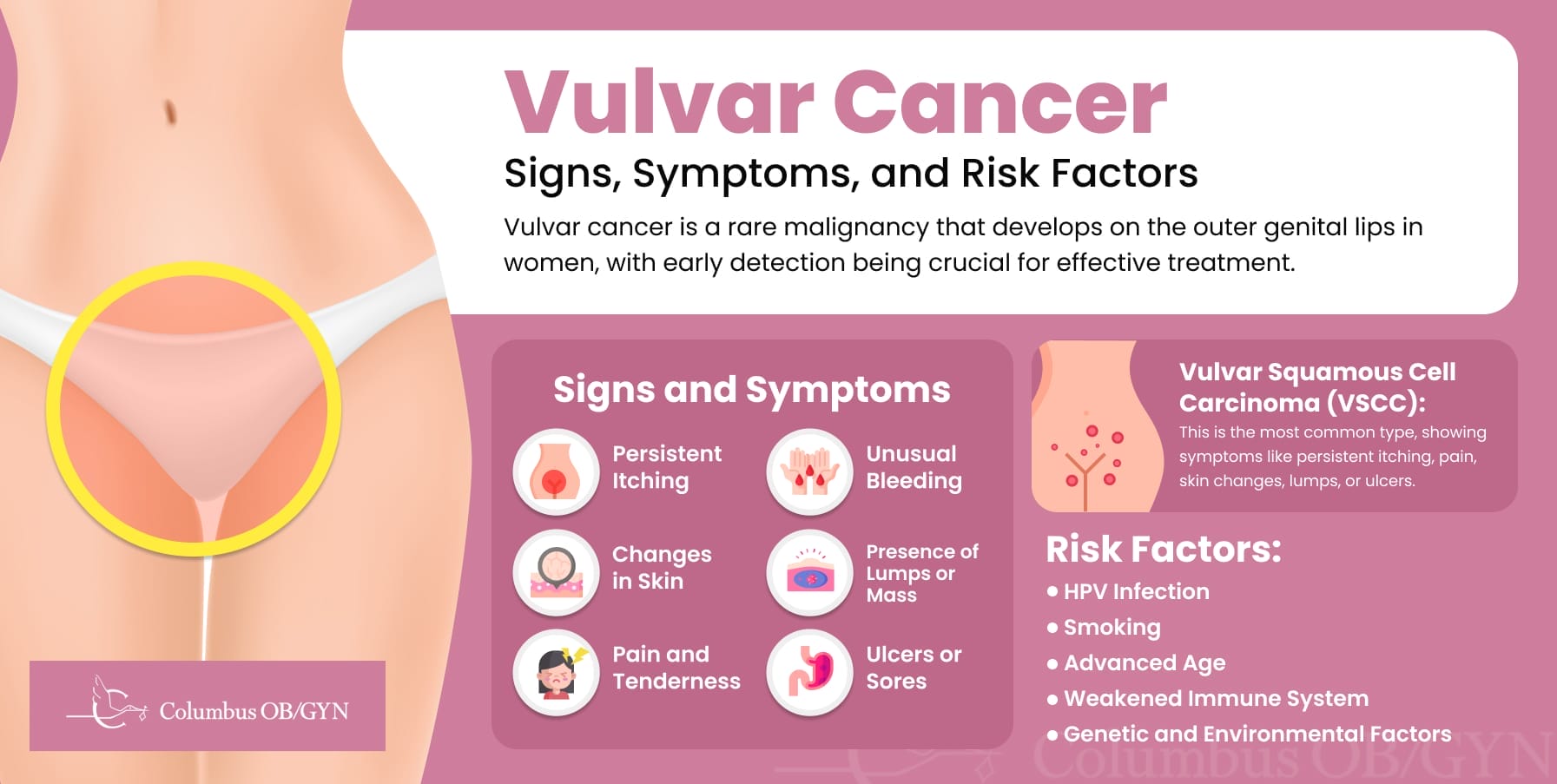
Vulvar cancers are primarily categorized based on the type of cells in which they begin. The most common type, vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (VSCC), originates in the thin, flat cells lining the surface of the vulva and accounts for approximately 90% of all cases.
Other less common types of vulvar cancer include, all of which present unique characteristics and challenges in treatment:
Gynecologists in Lewis Center, OH, emphasize the importance of being vigilant about changes in the vulvar region, including persistent itching, pain, or the presence of lumps or lesions, as these can be early warning signs of cell changes.
Vulvar cancer’s symptoms can be diverse, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and prompt medical consultation. Key symptoms include:
The symptom that can be particularly concerning is the presence of a lump or mass on the vulva that can be felt, which indicates abnormal cells.
This lump might be painless at first, which can lead some to delay seeking medical evaluation in Hilliard.
However, any new lump or growth should be examined by a healthcare professional.
Ulcers or sores that do not heal on their own over a period of weeks are another symptom that should prompt a visit to the doctor.
These signs can easily be mistaken for less serious conditions, like infections or skin conditions, which is why they are often overlooked until they become more severe.
Risk factors for developing vulvar cancer include persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV), smoking, advanced age, and conditions that lead to a weakened immune system.
Additionally, genetic and environmental factors may play a role, suggesting a multifaceted origin that requires further research for a comprehensive understanding for a proper vulvar cancer prognosis.
Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinomas (VSCC) merits particular attention since it is so common.
This form of vulvar cancer often presents symptoms that, while potentially subtle, serve as critical early warning signs, such as:
Early recognition of these and other symptoms is critical when it comes to seeking timely medical advice and intervention from your primary care doctor.
The diagnostic process for VSCC typically involves a thorough physical examination, biopsy, and possibly imaging tests to assess the extent of the cancer.
Staging, a crucial aspect of the diagnostic process, determines the cancer’s size, depth of invasion, and whether it has spread, which then guides the treatment plan.
Essentially, paying attention to your body and consulting your doctor are two of the best things you can do to prevent vulvar and other vaginal cancers.

Effective treatment for vulvar cancer typically involves a combination of strategies, tailored to the individual’s condition and the stage of cancer.
The main treatment options include:
Aimed at removing the cancerous tissue while preserving as much of the surrounding skin as possible.
Options range from local excision for smaller tumors to partial or complete vulvectomy for more extensive cases, again with the goal of preserving the surrounding healthy tissue.
Used to target and destroy cancer cells, often employed when surgery is not feasible or as an adjunct to surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
Recommended for advanced cases or when cancer has spread, utilizing drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
New and evolving treatments that offer hope for improved outcomes.
Although not all cases of vulvar or cervical cancer itself can be prevented, these strategies can contribute to reducing your overall risk of vulvar cancer and ensuring early intervention when necessary.
Knowing the warning signs of vulvar cancer is a proactive step that can significantly impact a woman’s health.
It’s important to act promptly at any signs of concern and communicate openly with healthcare professionals.
Remember, recognizing and acknowledging early warning signs is often the first defense, not just against vulvar cancer, but for many other health conditions as well.