
A lot of us don’t realize that some sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can silently threaten our fertility, causing damage before we even know anything’s wrong. Chlamydia is one of the most concerning of these infections. It’s often called a “silent” infection because it frequently causes no symptoms, yet it can lead to serious complications, including infertility.
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in the United States. The CDC estimates that more than 2.4 million people are infected each year, according to the latest data from 2023. What makes this sexually transmitted infection particularly dangerous is that up to 95% of women and 90% of men with chlamydia experience no symptoms at all.
This means you could have a chlamydia infection and not know it, allowing the bacteria to quietly damage your reproductive organs over time. The longer untreated chlamydia remains in your system, the more severe the complications can become.
Yes, chlamydia can cause infertility—but only if it goes untreated.
Here’s how this sexually transmitted infection can impact your reproductive health:
When chlamydia bacteria enter your reproductive system, they can travel from the cervix upward to infect the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. This ascending infection can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a serious condition that affects your fertility in several ways.
Your fallopian tubes play a crucial role in fertility—they’re where the fertilized egg travels from your ovaries to your uterus. When chlamydia causes inflammation in these delicate tubes, it can result in scarring and blockages. This scarring can prevent the fertilized egg from moving through the tubes properly, leading to:
One of the most serious complications of untreated chlamydia is an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy. When scarring from a chlamydia infection partially blocks the fallopian tubes, a fertilized egg may become stuck and begin to develop in the tube rather than continuing to the uterus where it belongs.
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. This is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention and can result in the loss of the affected fallopian tube.
Pelvic inflammatory disease is perhaps the most serious complication of untreated chlamydia. PID occurs when the infection spreads beyond the cervix to affect the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. This condition can cause:
The CDC reports that even one episode of PID can reduce fertility, and repeated episodes significantly increase the risk of permanent damage.

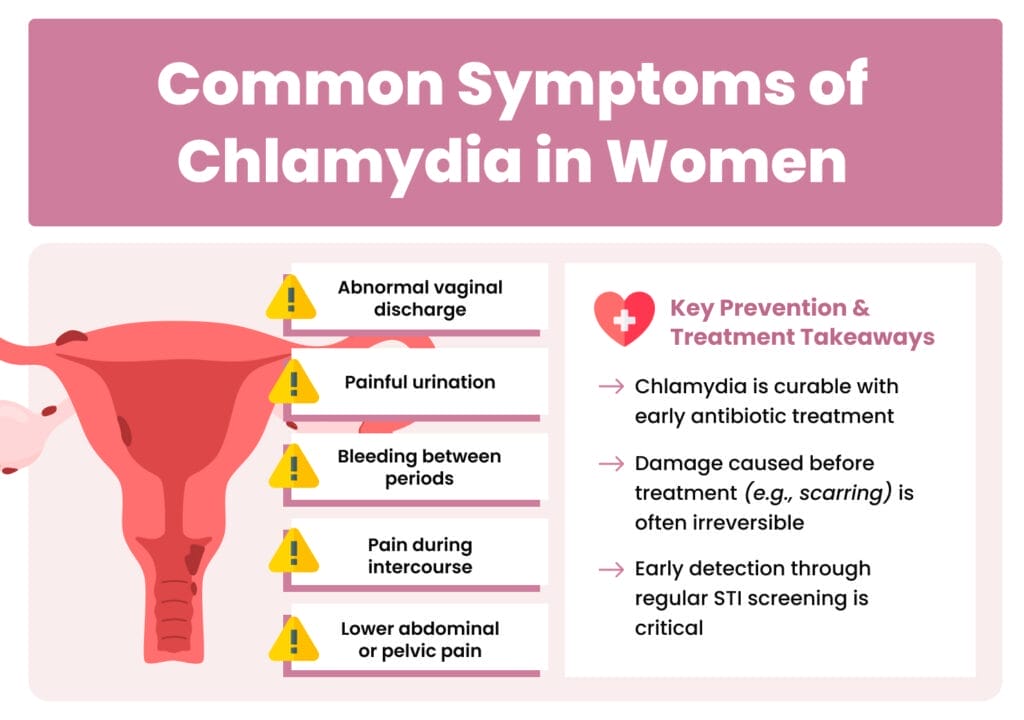
While chlamydia often produces no symptoms, some women may experience:
These symptoms usually appear within one to three weeks after infection but may be very mild or mistaken for other conditions.
Related Article: Can Birth Control Cause Infertility?
Having chlamydia also increases your risk of contracting other sexually transmitted diseases, including gonorrhea and HIV. Gonorrhea can cause similar fertility complications, and having multiple STIs can compound the damage to your reproductive organs.
Related Article: What Causes Infertility in Women?
The good news is that chlamydia is completely curable with antibiotics when caught early. Simple antibiotic treatment can eliminate the infection before it causes permanent damage to your fertility. Common antibiotics used include azithromycin or doxycycline.
However, it’s crucial to understand that while antibiotics can cure the infection, they cannot reverse any scarring or damage that has already occurred to your reproductive organs. This is why early detection and treatment are so important.

To protect your fertility from chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections:
If you’re sexually active, don’t wait for symptoms to appear. Regular screening is the best way to catch chlamydia before it can cause complications. Contact your healthcare provider or OB/GYN immediately if you experience pelvic pain, unusual discharge, or other concerning symptoms.
Remember, untreated chlamydia can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system, but when caught early, it’s completely treatable. Don’t let this preventable cause of infertility affect your future family planning—talk to your doctor about regular STI screening today.